Optimize Your Wi-Fi on Windows With Preferred Band Settings Leave a comment
Wi-Fi networks generally operate on two frequency bands: 2.4GHz and 5GHz. Here’s how to choose between them.
How Do 2.4GHz and 5GHz Bands Differ?
Both bands work well for an average user, but each has its strengths and limitations. Depending on the situation, switching to a specific band can improve your Wi-Fi performance.
The 2.4GHz band offers a wider coverage area and better penetration through walls and obstacles, making it an ideal frequency band for maintaining a stable connection over longer distances.
On the other hand, the 5GHz frequency band has a shorter range and is less effective at penetrating walls and obstacles, but is less prone to interference.
This is because many household devices, such as microwaves, baby monitors, and cordless phones, operate using the 2.4GHz frequency. This makes this band more prone to interference, while the 5GHz band experiences less interference due to fewer devices using it.
This means you can often rely on 5GHz bands to provide a more stable connection, so long as there aren’t a lot of walls or obstacles between the router and your device.
The 5GHz band also supports faster data transfer rates because of less interference. The 2.4GHz band, however, is slower due to congestion from other devices.
When Should You Use 2.4GHz vs. 5GHz?
Based on how the bands work, you should choose the 2.4GHz band if you need Wi-Fi to cover a larger area. This is ideal if your device is far from the router, there are many walls or obstacles between the router and your computer, or you’re only using the internet for basic tasks like browsing or checking emails.
Avoid using the 2.4GHz band if you have other nearby devices operating at the same frequency, as they could cause interference.
The 5GHz band is better if your device is close to the router with few barriers in between. It lets you maintain a more stable connection and avoids interference from 2.4GHz devices. This band is also ideal for activities that need faster speeds, like gaming, HD video streaming, or transferring large files.
How to Set Your Preferred Band in Windows
By default, the network adapter automatically selects the band with the best available signal based on your distance from your router and other factors.
However, if you’ve determined which band suits your needs and the layout of your home or office, you can easily switch to your preferred band on Windows in just a few steps:
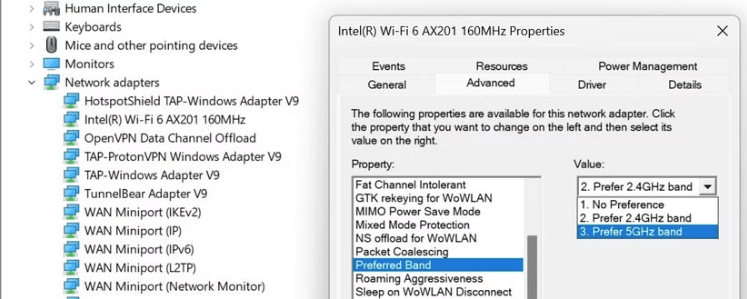
- Right-click the Start button and select Device Manager.
- Expand the Network adapters category and locate your network adapter.
- Right-click your network adapter and select Properties.
- In the Properties window, go to the Advanced tab.
- Look for the option labeled Preferred Band or simply Band in the Property list.
- In the Value dropdown, you’ll likely see it set to No Preference.
- Select your desired band, 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz, based on your needs, click OK, and restart your device for the changes to apply.
I keep my frequency band set to No Preference since I frequently move my laptop between rooms, and each frequency band works better in different areas.
No single band is perfect for every situation. You should test both bands to find out which one best suits your situation and needs.
This saves me the hassle of constantly switching bands. However, when I need faster speeds or a stable connection, I switch to a specific band for better performance.
Switching the frequency band can improve both connection stability and speed. However, fine-tuning other Wi-Fi settings is equally important for achieving the best performance.
